
Potato
Potatoes, mashed, dehydrated, prepared from granules with milk, water and margarine added
116 kcal
Energy
4.8 g
Fat
1.2 g
Saturates
1.7 g
Sugar
0.4 g
Salt
Caloric Ratio
Nutrition
| Calories % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Calories | 116 (486 kJ) | |
| from Carbohydrate | 65 (270 kJ) | |
| from Fat | 43 (181 kJ) | |
| from Protein | 9 (36 kJ) | |
| from Alcohol | 0 (0 kJ) | |
| Carbohydrates % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Carbohydrates | 16.1 g | |
| Dietary Fiber | 1.3 g | |
| Starch | ~ | |
| Sugars | 1.7 g | |
| Sucrose | 180.0 mg | |
| Glucose | 160.0 mg | |
| Fructose | 180.0 mg | |
| Lactose | 1,090.0 mg | |
| Maltose | 90.0 mg | |
| Galactose | 0.0 mg | |
| Fats & Fatty Acids % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Fat | 4.8 g | |
| Saturated Fat | 1.2 g | |
| Butyric Acid | 16.0 mg | |
| Caproic Acid | 16.0 mg | |
| Caprylic Acid | 16.0 mg | |
| Capric Acid | 17.0 mg | |
| Lauric Acid | 20.0 mg | |
| Tridecylic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Myristic Acid | 67.0 mg | |
| Pentadecanoic Acid | 1.0 mg | |
| Palmitic Acid | 613.0 mg | |
| Margaric Acid | 3.0 mg | |
| Stearic Acid | 389.0 mg | |
| Arachidic Acid | 13.0 mg | |
| Behenic Acid | 5.0 mg | |
| Lignoceric Acid | 4.0 mg | |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 2.1 g | |
| Myristoleic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| 15:1 | 0.0 mg | |
| Palmitoleic Acid | 3.0 mg | |
| 16:1 c | ~ | |
| 16:1 t | ~ | |
| 17:1 | 1.0 mg | |
| Oleic Acid | 2,097.0 mg | |
| 18:1 c | ~ | |
| 18:1 t | ~ | |
| Gadoleic Acid | 7.0 mg | |
| Erucic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| 22:1 c | ~ | |
| 22:1 t | ~ | |
| Nervonic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 1.3 g | |
| Linoleic Acid | 1,163.0 mg | |
| 18:2 CLAs | ~ | |
| 18:2 n-6 c,c | ~ | |
| 18:2 t,t | ~ | |
| 18:2 i | ~ | |
| 18:2 t | ~ | |
| Linolenic Acid | 127.0 mg | |
| alpha-Linolenic Acid | ~ | |
| gamma-Linolenic acid | ~ | |
| Parinaric Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Eicosadienoic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Eicosatrienoic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| 20:3 n-3 | ~ | |
| Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid | ~ | |
| Arachidonic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| 20:4 n-6 | ~ | |
| Timnodonic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Clupanodonic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Docosahexaenoic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Trans Fat | 0.6 g | |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | 127.0 mg | |
| Omega-6 Fatty Acids | 1,163.0 mg | |
| Sterols % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol | 2.0 mg | |
| Phytosterols | 20.0 mg | |
| Campesterol | ~ | |
| Stigmasterol | ~ | |
| Beta-sitosterol | ~ | |
| Protein & Amino Acids % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 2.1 g | |
| Essential Aminos | ||
| Histidine | 44.0 mg | |
| Isoleucine | 87.0 mg | |
| Leucine | 137.0 mg | |
| Lysine | 116.0 mg | |
| Methionine | 40.0 mg | |
| Phenylalanine | 123.0 mg | |
| Threonine | 81.0 mg | |
| Tryptophan | 31.0 mg | |
| Valine | 121.0 mg | |
| Non-essential Aminos | ||
| Alanine | 75.0 mg | |
| Arginine | 96.0 mg | |
| Aspartic Acid | 392.0 mg | |
| Cystine | 24.0 mg | |
| Glutamic Acid | 404.0 mg | |
| Glycine | 61.0 mg | |
| Proline | 126.0 mg | |
| Serine | 84.0 mg | |
| Tyrosine | 75.0 mg | |
| Other Nutrients % Daily Value | |
|---|---|
| Alcohol | 0.0 g |
| Water | 76.0 g |
| Ash | 0.9 g |
| Caffiene | 0.0 mg |
| Theobromine | 0.0 mg |
| Vitamins % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Betaine | ~ | |
| Choline | 13.7 mg | |
| Vitamin A | 214 IU | |
| Vitamin B1 (thiamine) | 0.1 mg | |
| Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | 0.1 mg | |
| Vitamin B3 (niacin) | 0.9 mg | |
| Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) | 0.1 mg | |
| Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | 0.2 mg | |
| Vitamin B9 (folate) | 8 mcg | |
| Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) | 0 mcg | |
| Vitamin C | 6.5 mg | |
| Vitamin D | 11 IU | |
| Vitamin E | 1 IU | |
| Vitamin K | 6 mcg | |
| Minerals % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 35.0 mg | |
| Copper | 0.0 mg | |
| Fluoride | 39.6 mcg | |
| Iron | 0.2 mg | |
| Magnesium | 20.0 mg | |
| Manganese | 0.2 mg | |
| Phosphorus | 62.0 mg | |
| Potassium | 155.0 mg | |
| Sodium | 172.0 mg | |
| Zinc | 0.2 mg | |
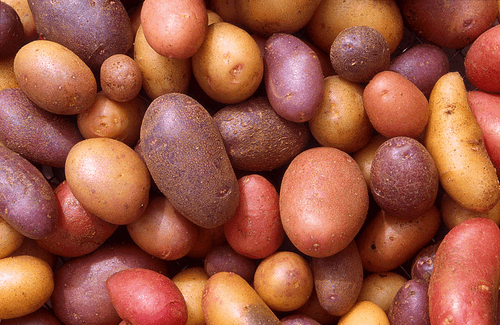
About Potato
The potato is a starchy, tuberous crop from the perennial Solanum tuberosum of the Solanaceae family (also known as the nightshades). The word may refer to the plant itself as well as the edible tuber. In the region of the Andes, there are some other closely related cultivated potato species. Potatoes were introduced outside the Andes region four centuries ago, and have become an integral part of much of the world's cuisine. It is the world's fourth-largest food crop, following rice, wheat and maize. Read More
The potato is a starchy, tuberous crop from the perennial Solanum tuberosum of the Solanaceae family (also known as the nightshades). The word may refer to the plant itself as well as the edible tuber. In the region of the Andes, there are some other closely related cultivated potato species. Potatoes were introduced outside the Andes region four centuries ago, and have become an integral part of much of the world's cuisine. It is the world's fourth-largest food crop, following rice, wheat and maize. Long-term storage of potatoes requires specialised care in cold warehouses. Wild potato species occur throughout the Americas, from the United States to southern Chile. The potato was originally believed to have been domesticated independently in multiple locations, but later genetic testing of the wide variety of cultivars and wild species proved a single origin for potatoes in the area of present-day southern Peru and extreme northwestern Bolivia (from a species in the Solanum brevicaule complex), where they were domesticated 7,000–10,000 years ago. Following centuries of selective breeding, there are now over a thousand different types of potatoes. Of these subspecies, a variety that at one point grew in the Chiloé Archipelago left its germplasm on over 99% of the cultivated potatoes worldwide. The annual diet of an average global citizen in the first decade of the 21st century included about 33 kg of potato. However, the local importance of potato is extremely variable and rapidly changing. It remains an essential crop in Europe (especially eastern and central Europe), where per capita production is still the highest in the world, but the most rapid expansion over the past few decades has occurred in southern and eastern Asia. China is now the world's largest potato-producing country, and nearly a third of the world's potatoes are harvested in China and India.