Shark
Fish, shark, mixed species, cooked, batter-dipped and fried
228 kcal
Energy
13.8 g
Fat
3.2 g
Saturates
0.3 g
Salt
Caloric Ratio
Nutrition
| Calories % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Calories | 228 (954 kJ) | |
| from Carbohydrate | 26 (107 kJ) | |
| from Fat | 124 (521 kJ) | |
| from Protein | 74 (312 kJ) | |
| from Alcohol | 0 (0 kJ) | |
| Carbohydrates % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Carbohydrates | 6.4 g | |
| Dietary Fiber | 0.0 g | |
| Starch | ~ | |
| Sugars | ~ | |
| Sucrose | ~ | |
| Glucose | ~ | |
| Fructose | ~ | |
| Lactose | ~ | |
| Maltose | ~ | |
| Galactose | ~ | |
| Fats & Fatty Acids % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Fat | 13.8 g | |
| Saturated Fat | 3.2 g | |
| Butyric Acid | ~ | |
| Caproic Acid | ~ | |
| Caprylic Acid | ~ | |
| Capric Acid | ~ | |
| Lauric Acid | ~ | |
| Tridecylic Acid | ~ | |
| Myristic Acid | 102.0 mg | |
| Pentadecanoic Acid | ~ | |
| Palmitic Acid | 2,008.0 mg | |
| Margaric Acid | ~ | |
| Stearic Acid | 1,092.0 mg | |
| Arachidic Acid | ~ | |
| Behenic Acid | ~ | |
| Lignoceric Acid | ~ | |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 5.9 g | |
| Myristoleic Acid | ~ | |
| 15:1 | ~ | |
| Palmitoleic Acid | 223.0 mg | |
| 16:1 c | ~ | |
| 16:1 t | ~ | |
| 17:1 | ~ | |
| Oleic Acid | 5,216.0 mg | |
| 18:1 c | ~ | |
| 18:1 t | ~ | |
| Gadoleic Acid | 217.0 mg | |
| Erucic Acid | 253.0 mg | |
| 22:1 c | ~ | |
| 22:1 t | ~ | |
| Nervonic Acid | ~ | |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 3.7 g | |
| Linoleic Acid | 2,600.0 mg | |
| 18:2 CLAs | ~ | |
| 18:2 n-6 c,c | ~ | |
| 18:2 t,t | ~ | |
| 18:2 i | ~ | |
| 18:2 t | ~ | |
| Linolenic Acid | 190.0 mg | |
| alpha-Linolenic Acid | ~ | |
| gamma-Linolenic acid | ~ | |
| Parinaric Acid | 25.0 mg | |
| Eicosadienoic Acid | ~ | |
| Eicosatrienoic Acid | ~ | |
| 20:3 n-3 | ~ | |
| Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid | ~ | |
| Arachidonic Acid | 92.0 mg | |
| 20:4 n-6 | ~ | |
| Timnodonic Acid | 258.0 mg | |
| Clupanodonic Acid | 89.0 mg | |
| Docosahexaenoic Acid | 431.0 mg | |
| Trans Fat | ~ | |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | 190.0 mg | |
| Omega-6 Fatty Acids | 2,600.0 mg | |
| Sterols % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol | 59.0 mg | |
| Phytosterols | ~ | |
| Campesterol | ~ | |
| Stigmasterol | ~ | |
| Beta-sitosterol | ~ | |
| Protein & Amino Acids % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 18.6 g | |
| Essential Aminos | ||
| Histidine | 538.0 mg | |
| Isoleucine | 867.0 mg | |
| Leucine | 1,515.0 mg | |
| Lysine | 1,634.0 mg | |
| Methionine | 541.0 mg | |
| Phenylalanine | 750.0 mg | |
| Threonine | 843.0 mg | |
| Tryptophan | 212.0 mg | |
| Valine | 965.0 mg | |
| Non-essential Aminos | ||
| Alanine | 1,097.0 mg | |
| Arginine | 1,094.0 mg | |
| Aspartic Acid | 1,850.0 mg | |
| Cystine | 212.0 mg | |
| Glutamic Acid | 2,970.0 mg | |
| Glycine | 872.0 mg | |
| Proline | 744.0 mg | |
| Serine | 789.0 mg | |
| Tyrosine | 633.0 mg | |
| Other Nutrients % Daily Value | |
|---|---|
| Alcohol | ~ |
| Water | 60.1 g |
| Ash | 1.3 g |
| Caffiene | ~ |
| Theobromine | ~ |
| Vitamins % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Betaine | ~ | |
| Choline | ~ | |
| Vitamin A | 180 IU | |
| Vitamin B1 (thiamine) | 0.1 mg | |
| Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | 0.1 mg | |
| Vitamin B3 (niacin) | 2.8 mg | |
| Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) | 0.6 mg | |
| Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | 0.3 mg | |
| Vitamin B9 (folate) | 15 mcg | |
| Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) | 1 mcg | |
| Vitamin C | 0.0 mg | |
| Vitamin D | ~ | |
| Vitamin E | ~ | |
| Vitamin K | ~ | |
| Minerals % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 50.0 mg | |
| Copper | 0.0 mg | |
| Fluoride | ~ | |
| Iron | 1.1 mg | |
| Magnesium | 43.0 mg | |
| Manganese | 0.1 mg | |
| Phosphorus | 194.0 mg | |
| Potassium | 155.0 mg | |
| Sodium | 122.0 mg | |
| Zinc | 0.5 mg | |
About Shark
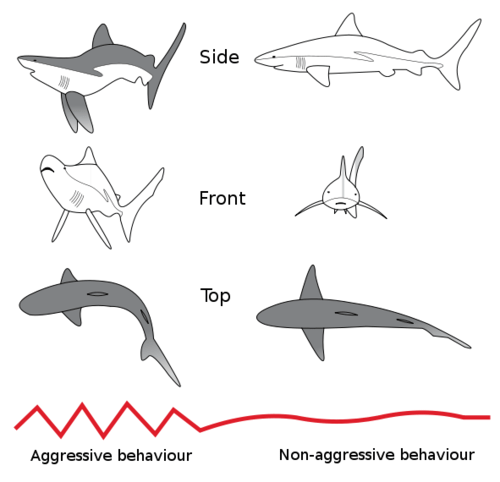
Sharks are a group of fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimorpha (or Selachii) and are the sister group to the rays. However, the term "shark" has also been used for extinct members of the subclass Elasmobranchii outside the Selachimorpha, such as Cladoselache and Xenacanthus. Under this broader definition, the earliest known sharks date from more than 420 million years ago. Since then, sharks have diversified into over 470 species. Read More
Sharks are a group of fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimorpha (or Selachii) and are the sister group to the rays. However, the term "shark" has also been used for extinct members of the subclass Elasmobranchii outside the Selachimorpha, such as Cladoselache and Xenacanthus. Under this broader definition, the earliest known sharks date from more than 420 million years ago. Since then, sharks have diversified into over 470 species. They range in size from the small dwarf lanternshark (Etmopterus perryi), a deep sea species of only 17 centimetres (6.7 in) in length, to the whale shark (Rhincodon typus), the largest fish in the world, which reaches approximately 12 metres (39 ft). Sharks are found in all seas and are common to depths of 2,000 metres (6,600 ft). They generally do not live in freshwater although there are a few known exceptions, such as the bull shark and the river shark, which can survive in both seawater and freshwater. They breathe through five to seven gill slits. Sharks have a covering of dermal denticles that protects their skin from damage and parasites in addition to improving their fluid dynamics. They have several sets of replaceable teeth. Well-known species such as the great white shark, tiger shark, blue shark, mako shark, and the hammerhead shark are apex predators?organisms at the top of their underwater food chain.