About Northern Bluefin Tuna
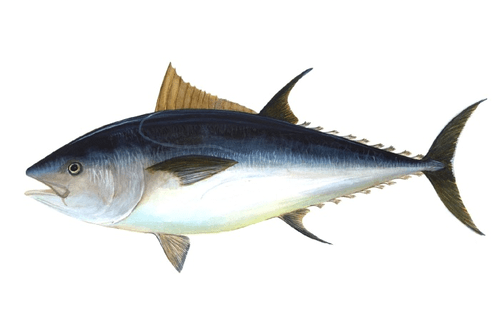
The Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) is a species of tuna in the Scombridae family. It is variously known as the northern bluefin tuna (mainly when including Pacific bluefin as a subspecies), giant bluefin tuna (for individuals exceeding 150 kilograms or around 330 pounds) and formerly as the tunny. Atlantic bluefin are native to both the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, as well as the Mediterranean Sea. Atlantic bluefin have become extinct in the Black Sea. The Atlantic bluefin tuna is a close relative of the other two bluefin tuna species—the Pacific bluefin tuna and the southern bluefin tuna. Read More
The Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) is a species of tuna in the Scombridae family. It is variously known as the northern bluefin tuna (mainly when including Pacific bluefin as a subspecies), giant bluefin tuna (for individuals exceeding 150 kilograms or around 330 pounds) and formerly as the tunny. Atlantic bluefin are native to both the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, as well as the Mediterranean Sea. Atlantic bluefin have become extinct in the Black Sea. The Atlantic bluefin tuna is a close relative of the other two bluefin tuna species—the Pacific bluefin tuna and the southern bluefin tuna. Atlantic bluefin tuna may exceed 450 kilograms in weight, and rival the black marlin, blue marlin and swordfish as the largest Perciformes. Throughout recorded history, the Atlantic bluefin tuna has been highly prized as a food fish. Besides their commercial value as food, the great size, speed, and power they display as apex predators has attracted the admiration of fishermen, writers, and scientists. The Atlantic bluefin tuna has been the foundation of one of the world's most lucrative commercial fisheries. Medium-sized and large individuals are heavily targeted for the Japanese raw fish market, where all bluefin species are highly prized for sushi and sashimi. This commercial importance has led to severe overfishing. The International Commission for the Conservation of Atlantic Tunas (ICCAT) affirmed in October 2009 that Atlantic bluefin tuna stocks have declined dramatically over the last 40 years, by 72% in the Eastern Atlantic, and by 82% in the Western Atlantic. On 16 October 2009, Monaco formally recommended Endangered Atlantic bluefin tuna for an Appendix I CITES listing and international trade ban. In early 2010, European officials, led by the French ecology minister, increased pressure to ban the commercial fishing of bluefin tuna internationally. European Union nations, who are responsible for most bluefin tuna overfishing, later abstained from voting to protect the species from international trade. Most Bluefin are captured commercially by professional fishermen using longlines; purse seines, assorted hook-and-line gear, heavy rod and reels, and harpoon. Recreationally, bluefin has been one of the most important big-game species sought by sports fishermen since the 1930s, particularly in the United States but also in Canada, Spain, France and Italy.