313 kcal
Energy
8.4 g
Fat
2.3 g
Saturates
0.1 g
Salt
Caloric Ratio
Nutrition
| Calories % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Calories | 313 (1312 kJ) | |
| from Carbohydrate | 300 (1256 kJ) | |
| from Fat | 75 (315 kJ) | |
| from Protein | 30 (127 kJ) | |
| from Alcohol | 0 (0 kJ) | |
| Carbohydrates % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Carbohydrates | 75.0 g | |
| Dietary Fiber | 26.3 g | |
| Starch | ~ | |
| Sugars | ~ | |
| Sucrose | ~ | |
| Glucose | ~ | |
| Fructose | ~ | |
| Lactose | ~ | |
| Maltose | ~ | |
| Galactose | ~ | |
| Fats & Fatty Acids % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Fat | 8.4 g | |
| Saturated Fat | 2.3 g | |
| Butyric Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Caproic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Caprylic Acid | 10.0 mg | |
| Capric Acid | 10.0 mg | |
| Lauric Acid | 530.0 mg | |
| Tridecylic Acid | ~ | |
| Myristic Acid | 210.0 mg | |
| Pentadecanoic Acid | ~ | |
| Palmitic Acid | 1,270.0 mg | |
| Margaric Acid | ~ | |
| Stearic Acid | 160.0 mg | |
| Arachidic Acid | ~ | |
| Behenic Acid | ~ | |
| Lignoceric Acid | ~ | |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 1.6 g | |
| Myristoleic Acid | ~ | |
| 15:1 | ~ | |
| Palmitoleic Acid | 140.0 mg | |
| 16:1 c | ~ | |
| 16:1 t | ~ | |
| 17:1 | ~ | |
| Oleic Acid | 1,500.0 mg | |
| 18:1 c | ~ | |
| 18:1 t | ~ | |
| Gadoleic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Erucic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| 22:1 c | ~ | |
| 22:1 t | ~ | |
| Nervonic Acid | ~ | |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 2.3 g | |
| Linoleic Acid | 1,240.0 mg | |
| 18:2 CLAs | ~ | |
| 18:2 n-6 c,c | ~ | |
| 18:2 t,t | ~ | |
| 18:2 i | ~ | |
| 18:2 t | ~ | |
| Linolenic Acid | 1,050.0 mg | |
| alpha-Linolenic Acid | ~ | |
| gamma-Linolenic acid | ~ | |
| Parinaric Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Eicosadienoic Acid | ~ | |
| Eicosatrienoic Acid | ~ | |
| 20:3 n-3 | ~ | |
| Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid | ~ | |
| Arachidonic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| 20:4 n-6 | ~ | |
| Timnodonic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Clupanodonic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Docosahexaenoic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Trans Fat | 0.0 g | |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | 1,050.0 mg | |
| Omega-6 Fatty Acids | 1,240.0 mg | |
| Sterols % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol | 0.0 mg | |
| Phytosterols | ~ | |
| Campesterol | ~ | |
| Stigmasterol | ~ | |
| Beta-sitosterol | ~ | |
| Protein & Amino Acids % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 7.6 g | |
| Essential Aminos | ||
| Histidine | ~ | |
| Isoleucine | ~ | |
| Leucine | ~ | |
| Lysine | ~ | |
| Methionine | ~ | |
| Phenylalanine | ~ | |
| Threonine | ~ | |
| Tryptophan | ~ | |
| Valine | ~ | |
| Non-essential Aminos | ||
| Alanine | ~ | |
| Arginine | ~ | |
| Aspartic Acid | ~ | |
| Cystine | ~ | |
| Glutamic Acid | ~ | |
| Glycine | ~ | |
| Proline | ~ | |
| Serine | ~ | |
| Tyrosine | ~ | |
| Other Nutrients % Daily Value | |
|---|---|
| Alcohol | 0.0 g |
| Water | 5.4 g |
| Ash | 3.6 g |
| Caffiene | ~ |
| Theobromine | ~ |
| Vitamins % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Betaine | ~ | |
| Choline | ~ | |
| Vitamin A | 6,185 IU | |
| Vitamin B1 (thiamine) | 0.0 mg | |
| Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | 0.4 mg | |
| Vitamin B3 (niacin) | 2.0 mg | |
| Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) | ~ | |
| Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | 1.7 mg | |
| Vitamin B9 (folate) | 180 mcg | |
| Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) | 0 mcg | |
| Vitamin C | 46.5 mg | |
| Vitamin D | 0 IU | |
| Vitamin E | ~ | |
| Vitamin K | ~ | |
| Minerals % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 834.0 mg | |
| Copper | 0.4 mg | |
| Fluoride | ~ | |
| Iron | 43.0 mg | |
| Magnesium | 120.0 mg | |
| Manganese | 8.2 mg | |
| Phosphorus | 113.0 mg | |
| Potassium | 529.0 mg | |
| Sodium | 23.0 mg | |
| Zinc | 3.7 mg | |
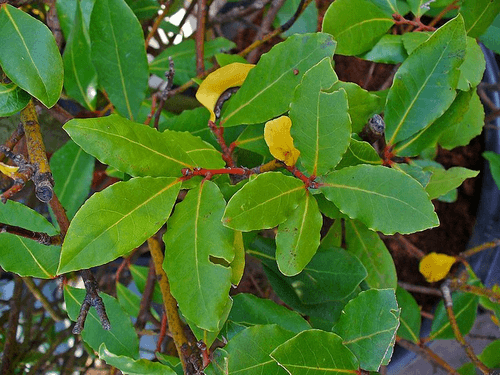
About Sweet Bay
Laurus nobilis is an aromatic evergreen tree or large shrub with green, glossy leaves, native to the Mediterranean region. It is one of the plants used for bay leaf seasoning in cooking. It is known as bay laurel, sweet bay, bay tree (esp. United Kingdom), true laurel, Grecian laurel, laurel tree or simply laurel. Laurus nobilis figures prominently in classical Greek, Roman, and Biblical culture. Read More
Laurus nobilis is an aromatic evergreen tree or large shrub with green, glossy leaves, native to the Mediterranean region. It is one of the plants used for bay leaf seasoning in cooking. It is known as bay laurel, sweet bay, bay tree (esp. United Kingdom), true laurel, Grecian laurel, laurel tree or simply laurel. Laurus nobilis figures prominently in classical Greek, Roman, and Biblical culture. The plant is the source of several popular herbs and one spice used in a wide variety of recipes, particularly among Mediterranean cuisines. Most commonly, the aromatic leaves are added whole to Italian pasta sauces. However, even when cooked, whole bay leaves can be sharp and abrasive enough to damage internal organs, so they are typically removed from dishes before serving, unless used as a simple garnish. Whole bay leaves have a long shelf life of about one year, under normal temperature and humidity. Bay leaves are used almost exclusively as flavor agents during the food preparation stage;
