16 kcal
Energy
0.1 g
Fat
0.0 g
Saturates
1.1 g
Sugar
0.1 g
Salt
Caloric Ratio
Nutrition
| Calories % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Calories | 16 (65 kJ) | |
| from Carbohydrate | 13 (55 kJ) | |
| from Fat | 0 (2 kJ) | |
| from Protein | 5 (23 kJ) | |
| from Alcohol | 0 (0 kJ) | |
| Carbohydrates % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Carbohydrates | 3.3 g | |
| Dietary Fiber | 2.0 g | |
| Starch | ~ | |
| Sugars | 1.1 g | |
| Sucrose | ~ | |
| Glucose | ~ | |
| Fructose | ~ | |
| Lactose | ~ | |
| Maltose | ~ | |
| Galactose | ~ | |
| Fats & Fatty Acids % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Fat | 0.1 g | |
| Saturated Fat | 0.0 g | |
| Butyric Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Caproic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Caprylic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Capric Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Lauric Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Tridecylic Acid | ~ | |
| Myristic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Pentadecanoic Acid | ~ | |
| Palmitic Acid | 5.0 mg | |
| Margaric Acid | ~ | |
| Stearic Acid | 1.0 mg | |
| Arachidic Acid | ~ | |
| Behenic Acid | ~ | |
| Lignoceric Acid | ~ | |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 0.0 g | |
| Myristoleic Acid | ~ | |
| 15:1 | ~ | |
| Palmitoleic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| 16:1 c | ~ | |
| 16:1 t | ~ | |
| 17:1 | ~ | |
| Oleic Acid | 7.0 mg | |
| 18:1 c | ~ | |
| 18:1 t | ~ | |
| Gadoleic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Erucic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| 22:1 c | ~ | |
| 22:1 t | ~ | |
| Nervonic Acid | ~ | |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 0.0 g | |
| Linoleic Acid | 19.0 mg | |
| 18:2 CLAs | ~ | |
| 18:2 n-6 c,c | ~ | |
| 18:2 t,t | ~ | |
| 18:2 i | ~ | |
| 18:2 t | ~ | |
| Linolenic Acid | 2.0 mg | |
| alpha-Linolenic Acid | ~ | |
| gamma-Linolenic acid | ~ | |
| Parinaric Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Eicosadienoic Acid | ~ | |
| Eicosatrienoic Acid | ~ | |
| 20:3 n-3 | ~ | |
| Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid | ~ | |
| Arachidonic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| 20:4 n-6 | ~ | |
| Timnodonic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Clupanodonic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Docosahexaenoic Acid | 0.0 mg | |
| Trans Fat | 0.0 g | |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | 2.0 mg | |
| Omega-6 Fatty Acids | 19.0 mg | |
| Sterols % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol | 0.0 mg | |
| Phytosterols | ~ | |
| Campesterol | ~ | |
| Stigmasterol | ~ | |
| Beta-sitosterol | ~ | |
| Protein & Amino Acids % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 1.4 g | |
| Essential Aminos | ||
| Histidine | 26.0 mg | |
| Isoleucine | 52.0 mg | |
| Leucine | 82.0 mg | |
| Lysine | 63.0 mg | |
| Methionine | 16.0 mg | |
| Phenylalanine | 52.0 mg | |
| Threonine | 42.0 mg | |
| Tryptophan | 14.0 mg | |
| Valine | 62.0 mg | |
| Non-essential Aminos | ||
| Alanine | 53.0 mg | |
| Arginine | 55.0 mg | |
| Aspartic Acid | 92.0 mg | |
| Cystine | 8.0 mg | |
| Glutamic Acid | 154.0 mg | |
| Glycine | 48.0 mg | |
| Proline | 45.0 mg | |
| Serine | 46.0 mg | |
| Tyrosine | 30.0 mg | |
| Other Nutrients % Daily Value | |
|---|---|
| Alcohol | 0.0 g |
| Water | 94.3 g |
| Ash | 1.0 g |
| Caffiene | 0.0 mg |
| Theobromine | 0.0 mg |
| Vitamins % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Betaine | ~ | |
| Choline | 7.1 mg | |
| Vitamin A | 443 IU | |
| Vitamin B1 (thiamine) | 0.0 mg | |
| Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | 0.0 mg | |
| Vitamin B3 (niacin) | 0.3 mg | |
| Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) | 0.2 mg | |
| Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | 0.1 mg | |
| Vitamin B9 (folate) | 3 mcg | |
| Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) | 0 mcg | |
| Vitamin C | 5.3 mg | |
| Vitamin D | 0 IU | |
| Vitamin E | 0 IU | |
| Vitamin K | 5 mcg | |
| Minerals % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 164.0 mg | |
| Copper | 0.0 mg | |
| Fluoride | ~ | |
| Iron | 0.5 mg | |
| Magnesium | 47.0 mg | |
| Manganese | 0.4 mg | |
| Phosphorus | 16.0 mg | |
| Potassium | 195.0 mg | |
| Sodium | 20.0 mg | |
| Zinc | 0.2 mg | |
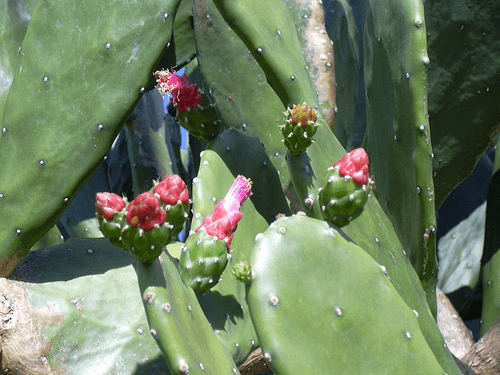
About Nopal
Nopales (for the pads) are a vegetable made from the young cladode (pad) segments of prickly pear, carefully peeled to remove the spines. These fleshy pads are flat and about hand-sized. They can be purple or green. They are particularly common in their native Mexico, where the plant is eaten commonly and regularly forms part of a variety of Mexican cuisine dishes. Farmed nopales are most often of the species Opuntia ficus-indica, although the pads of almost all Opuntia species are edible. Read More
Nopales (for the pads) are a vegetable made from the young cladode (pad) segments of prickly pear, carefully peeled to remove the spines. These fleshy pads are flat and about hand-sized. They can be purple or green. They are particularly common in their native Mexico, where the plant is eaten commonly and regularly forms part of a variety of Mexican cuisine dishes. Farmed nopales are most often of the species Opuntia ficus-indica, although the pads of almost all Opuntia species are edible. Nopales are generally sold fresh in Mexico. In more recent years bottled, or canned versions are available mostly for export. Less often dried versions are available. Used to prepare nopalitos, they have a light, slightly tart flavor, like green beans, and a crisp, mucilaginous texture. In most recipes the mucilaginous liquid they contain is included in the cooking. They are at their most tender and juicy in the spring. Nopales are most commonly used in Mexican cuisine in dishes such as huevos con nopales, carne con nopales (meat with nopal), tacos de nopales, or simply on their own or in salads with queso panela (panela cheese). Candied nopale is called acitróne. Nopales have also grown to be an important ingredient in New Mexican cuisine and in Tejano culture (Texas).
