901 kcal
Energy
100.0 g
Fat
30.4 g
Saturates
0.0 g
Salt
Caloric Ratio
Nutrition
| Calories % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Calories | 901 (3774 kJ) | |
| from Carbohydrate | 0 (0 kJ) | |
| from Fat | 900 (3768 kJ) | |
| from Protein | 0 (0 kJ) | |
| from Alcohol | 0 (0 kJ) | |
| Carbohydrates % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Carbohydrates | 0.0 g | |
| Dietary Fiber | 0.0 g | |
| Starch | ~ | |
| Sugars | ~ | |
| Sucrose | ~ | |
| Glucose | ~ | |
| Fructose | ~ | |
| Lactose | ~ | |
| Maltose | ~ | |
| Galactose | ~ | |
| Fats & Fatty Acids % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Total Fat | 100.0 g | |
| Saturated Fat | 30.4 g | |
| Butyric Acid | ~ | |
| Caproic Acid | ~ | |
| Caprylic Acid | ~ | |
| Capric Acid | ~ | |
| Lauric Acid | ~ | |
| Tridecylic Acid | ~ | |
| Myristic Acid | 7,958.0 mg | |
| Pentadecanoic Acid | ~ | |
| Palmitic Acid | 15,146.0 mg | |
| Margaric Acid | ~ | |
| Stearic Acid | 3,775.0 mg | |
| Arachidic Acid | ~ | |
| Behenic Acid | ~ | |
| Lignoceric Acid | ~ | |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 26.7 g | |
| Myristoleic Acid | ~ | |
| 15:1 | ~ | |
| Palmitoleic Acid | 10,482.0 mg | |
| 16:1 c | ~ | |
| 16:1 t | ~ | |
| 17:1 | ~ | |
| Oleic Acid | 14,527.0 mg | |
| 18:1 c | ~ | |
| 18:1 t | ~ | |
| Gadoleic Acid | 1,332.0 mg | |
| Erucic Acid | 352.0 mg | |
| 22:1 c | ~ | |
| 22:1 t | ~ | |
| Nervonic Acid | ~ | |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 34.2 g | |
| Linoleic Acid | 2,154.0 mg | |
| 18:2 CLAs | ~ | |
| 18:2 n-6 c,c | ~ | |
| 18:2 t,t | ~ | |
| 18:2 i | ~ | |
| 18:2 t | ~ | |
| Linolenic Acid | 1,490.0 mg | |
| alpha-Linolenic Acid | ~ | |
| gamma-Linolenic acid | ~ | |
| Parinaric Acid | 2,739.0 mg | |
| Eicosadienoic Acid | ~ | |
| Eicosatrienoic Acid | ~ | |
| 20:3 n-3 | ~ | |
| Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid | ~ | |
| Arachidonic Acid | 1,169.0 mg | |
| 20:4 n-6 | ~ | |
| Timnodonic Acid | 13,168.0 mg | |
| Clupanodonic Acid | 4,915.0 mg | |
| Docosahexaenoic Acid | 8,562.0 mg | |
| Trans Fat | ~ | |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | 1,490.0 mg | |
| Omega-6 Fatty Acids | 2,154.0 mg | |
| Sterols % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol | 521.0 mg | |
| Phytosterols | ~ | |
| Campesterol | ~ | |
| Stigmasterol | ~ | |
| Beta-sitosterol | ~ | |
| Protein & Amino Acids % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 0.0 g | |
| Essential Aminos | ||
| Histidine | ~ | |
| Isoleucine | ~ | |
| Leucine | ~ | |
| Lysine | ~ | |
| Methionine | ~ | |
| Phenylalanine | ~ | |
| Threonine | ~ | |
| Tryptophan | ~ | |
| Valine | ~ | |
| Non-essential Aminos | ||
| Alanine | ~ | |
| Arginine | ~ | |
| Aspartic Acid | ~ | |
| Cystine | ~ | |
| Glutamic Acid | ~ | |
| Glycine | ~ | |
| Proline | ~ | |
| Serine | ~ | |
| Tyrosine | ~ | |
| Other Nutrients % Daily Value | |
|---|---|
| Alcohol | ~ |
| Water | 0.0 g |
| Ash | 0.0 g |
| Caffiene | ~ |
| Theobromine | ~ |
| Vitamins % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Betaine | ~ | |
| Choline | ~ | |
| Vitamin A | 0 IU | |
| Vitamin B1 (thiamine) | 0.0 mg | |
| Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | 0.0 mg | |
| Vitamin B3 (niacin) | 0.0 mg | |
| Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) | 0.0 mg | |
| Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | 0.0 mg | |
| Vitamin B9 (folate) | 0 mcg | |
| Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) | 0 mcg | |
| Vitamin C | 0.0 mg | |
| Vitamin D | ~ | |
| Vitamin E | ~ | |
| Vitamin K | ~ | |
| Minerals % Daily Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 0.0 mg | |
| Copper | 0.0 mg | |
| Fluoride | ~ | |
| Iron | 0.0 mg | |
| Magnesium | 0.0 mg | |
| Manganese | 0.0 mg | |
| Phosphorus | 0.0 mg | |
| Potassium | 0.0 mg | |
| Sodium | 0.0 mg | |
| Zinc | 0.0 mg | |
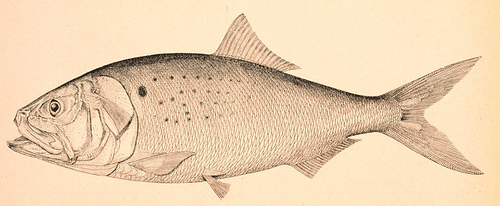
About Atlantic Menhaden
The Atlantic menhaden (Brevoortia tyrannus) is a silvery, highly compressed fish in the herring family, Clupeidae. A filter feeder, it lives on plankton caught in midwater. Adult fish can filter up to four gallons of water a minute; and they play an important role in clarifying ocean water. They are also a natural check to the deadly red tide. Menhaden have historically been used as a fertilizer for crops. Read More
The Atlantic menhaden (Brevoortia tyrannus) is a silvery, highly compressed fish in the herring family, Clupeidae. A filter feeder, it lives on plankton caught in midwater. Adult fish can filter up to four gallons of water a minute; and they play an important role in clarifying ocean water. They are also a natural check to the deadly red tide. Menhaden have historically been used as a fertilizer for crops. It is likely that menhaden is the fish that Squanto taught the Pilgrims to bury alongside freshly planted seeds as fertilizer. Other uses for menhaden include: feed for animals, bait for fish, oil for human consumption, oil for manufacturing purposes and oil as a fuel source. While many articles today state the menhaden as being inedible, the fish were once consumed as sardines or fried in early American history. Maine fisherman, for example, would eat fried pogies for breakfast. The fish that were not sold for bait would be sold to poorer classes for food. Menhaden historically occurred in large numbers in the North Atlantic, ranging from Nova Scotia, Canada to central Florida, USA, although their presence in northern waters has diminished in the 20th Century. They swim in large schools, some reportedly up to 40 miles long. As a result of their abundance they are important prey for a wide range of predators including bluefish, striped bass, cod, haddock, halibut, mackerel, swordfish, and tuna.